Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
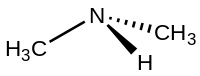
Dimethylamine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-Methylmethanamine | |
| Other names
(Dimethyl)amine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 605257 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.272 |
| EC Number |
|
| 849 | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | dimethylamine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1032 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties[1][2] | |
| (CH3)2NH | |
| Molar mass | 45.085 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| Odor | Fishy, ammoniacal |
| Density | 649.6 kg m−3 (at 25 °C) |
| Melting point | −93.00 °C; −135.40 °F; 180.15 K |
| Boiling point | 7 to 9 °C; 44 to 48 °F; 280 to 282 K |
| 1.540 kg L−1 | |
| log P | −0.362 |
| Vapor pressure | 170.3 kPa (at 20 °C) |
Henry's law
constant (kH) |
310 μmol Pa−1 kg−1 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 3.29 |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−21 to −17 kJ mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Danger | |
| H220, H302, H315, H318, H332, H335 | |
| P210, P261, P280, P305+P351+P338 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | −6 °C (21 °F; 267 K) (liquid) |
| 401 °C (754 °F; 674 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 2.8–14.4% |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
698 mg/kg (rat, oral) 316 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 240 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 240 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral)[4] |
LC50 (median concentration)
|
4700 ppm (rat, 4 hr) 4540 ppm (rat, 6 hr) 7650 ppm (mouse, 2 hr)[4] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 10 ppm (18 mg/m3)[3] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 10 ppm (18 mg/m3)[3] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
500 ppm[3] |
| Related compounds | |
Related amines
|
|
Related compounds
|
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2NH. This secondary amine is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%. An estimated 270,000 tons were produced in 2005.[5]
- ^ "Dimethylamine". NIST Chemistry WebBook. USA: National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 15 February 2022.
- ^ "Dimethylamine 38931 - ≥99.0%". Aldrich. Sigma-Aldrich Co. Retrieved 15 February 2022.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0219". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ a b "Dimethylamine". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Van Gysel, August B.; Musin, Willy (2000). "Methylamines". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a16_535. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2.
Previous Page Next Page



