
Back ديبيريدامول Arabic دی پیریدامول AZB Dipyridamol German Dipiridamol Spanish دی پیریدامول FA Dipyridamole French דיפירידאמול HE Dipiridamol Hungarian Dipiridamol ID Dipiridamolo Italian
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Persantine, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682830 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 37–66%[1] |
| Protein binding | ~99% |
| Metabolism | Liver (glucuronidation)[2] |
| Elimination half-life | α phase: 40 min, β phase: 10 hours |
| Excretion | Biliary (95%), urine (negligible) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.340 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
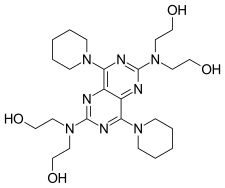
| Formula | C24H40N8O4 |
| Molar mass | 504.636 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Dipyridamole (trademarked as Persantine and others) is an antiplatelet drug of the nucleoside transport inhibitor and PDE3 inhibitor class that inhibits blood clot formation when given chronically and causes blood vessel dilation when given at high doses over a short time.
- ^ Nielsen-Kudsk F, Pedersen AK (May 1979). "Pharmacokinetics of dipyridamole". Acta Pharmacologica et Toxicologica. 44 (5): 391–399. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0773.1979.tb02350.x. PMID 474151.
- ^ "Aggrenox (aspirin/extended-release dipyridamole) Capsules. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Retrieved 1 December 2016.