Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Oscilloscope
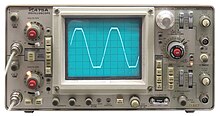


An oscilloscope (informally scope or O-scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying voltages of one or more signals as a function of time. Their main purpose is capturing information on electrical signals for debugging, analysis, or characterization. The displayed waveform can then be analyzed for properties such as amplitude, frequency, rise time, time interval, distortion, and others. Originally, calculation of these values required manually measuring the waveform against the scales built into the screen of the instrument.[1] Modern digital instruments may calculate and display these properties directly.
Oscilloscopes are used in the sciences, engineering, biomedical, automotive and the telecommunications industry. General-purpose instruments are used for maintenance of electronic equipment and laboratory work. Special-purpose oscilloscopes may be used to analyze an automotive ignition system or to display the waveform of the heartbeat as an electrocardiogram, for instance.
- ^ Kularatna, Nihal (2003), "Fundamentals of Oscilloscopes", Digital and Analogue Instrumentation: Testing and Measurement, Institution of Engineering and Technology, pp. 165–208, ISBN 978-0-85296-999-1
Previous Page Next Page


