Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Retinoid
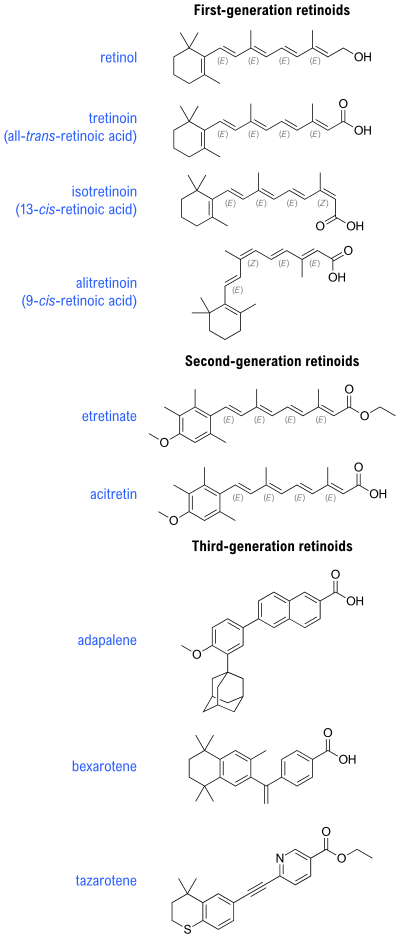
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are natural derivatives of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Synthetic retinoids are utilized in cosmetic formulations, clinical dermatology, and the treatment of some forms of cancer.[1]
Retinoids have many important functions throughout the body, including in vision,[2] regulation of skin proliferation and differentiation, growth of bone tissue, immune function,[3] and male fertility.[4]
The biology of retinoids is complex, having well-documented effectiveness in the management of conditions ranging from acute promyelocytic leukemia to acne to photoaging.[5] On the other hand, retinoids may be involved in metabolic dysfunction and, at least in some forms, carcinogenesis.[6][7]
- ^ Motamedi M, Chehade A, Sanghera R, Grewal P (2022). "A Clinician's Guide to Topical Retinoids". Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery. 26 (1): 71–78. doi:10.1177/12034754211035091. ISSN 1203-4754. PMC 8750127. PMID 34292058. Retrieved 30 Dec 2024.
- ^ Kiser PD, Golczak M, Palczewski K (January 2014). "Chemistry of the retinoid (visual) cycle". Chemical Reviews. 114 (1): 194–232. doi:10.1021/cr400107q. PMC 3858459. PMID 23905688.

- ^ Hall JA, Grainger JR, Spencer SP, Belkaid Y (July 2011). "The role of retinoic acid in tolerance and immunity". Immunity. 35 (1): 13–22. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.07.002. PMC 3418663. PMID 21777796.
- ^ Topping T, Griswold MD (2022-04-28). "Global Deletion of ALDH1A1 and ALDH1A2 Genes Does Not Affect Viability but Blocks Spermatogenesis". Frontiers in Endocrinology. 13: 871225. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.871225. PMC 9097449. PMID 35574006.
- ^ Nagai Y, Ambinder AJ (Jul 8, 2023). "The Promise of Retinoids in the Treatment of Cancer: Neither Burnt Out Nor Fading Away". Cancers. 15 (14): 3535. doi:10.3390/cancers15143535. ISSN 2072-6694. PMC 10377082. PMID 37509198.
- ^ Esposito M, Amory JK, Kang Y (September 2024). "The pathogenic role of retinoid nuclear receptor signaling in cancer and metabolic syndromes". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 221 (9): e20240519. doi:10.1084/jem.20240519. PMC 11318670. PMID 39133222.
- ^ Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, Balmes J, Cullen MR, Meyskens FL, Omenn GS, et al. (December 2004). "The Beta-Carotene and Retinol Efficacy Trial: incidence of lung cancer and cardiovascular disease mortality during 6-year follow-up after stopping beta-carotene and retinol supplements". Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 96 (23): 1743–1750. doi:10.1093/jnci/djh320. PMID 15572756.
Previous Page Next Page


