Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2007) |
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (October 2022) |
(Grand) Duchy of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (1809–1903) (Groß-)Herzogtum Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach Grand Duchy of Saxony (1903–1918) Großherzogtum Sachsen Free State of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (1918–1920) Freistaat Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1809–1920 | |||||||||||
| Anthem: Weimars Volkslied | |||||||||||
 Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach within the German Empire | |||||||||||
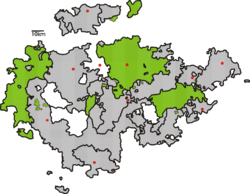 Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, shown within the Ernestine duchies | |||||||||||
| Status | State of the Confederation of the Rhine (1809–1813) State of the German Confederation (1815–1866) Federal State of the North German Confederation (1867–1871) Federal State of the German Empire (1871–1918) Federal State of the Weimar Republic (1918–1920) | ||||||||||
| Capital | Weimar | ||||||||||
| Common languages | German Thuringian dialect | ||||||||||
| Government | Absolute monarchy (1809–1816) Constitutional monarchy (1816–1918) Republic (1918–1920) | ||||||||||
| Grand Duke | |||||||||||
• 1809–1828 | Karl August (first) | ||||||||||
• 1901–1918 | William Ernest (last) | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||||
| 1741 | |||||||||||
• Merger of Eisenach and Weimar | September 20, 1809 | ||||||||||
• Raised to grand duchy | 1815 | ||||||||||
• German Revolution | 1918 | ||||||||||
• Joined Thuringia | 1920 | ||||||||||
| Currency | Saxon thaler (to 1857) Saxon Vereinsthaler (1857–1873) German gold mark (1873–1918) | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Germany | ||||||||||
Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (German: Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach) was a German state, created as a duchy in 1809 by the merger of the Ernestine duchies of Saxe-Weimar and Saxe-Eisenach, which had been in personal union since 1741. It was raised to a grand duchy in 1815 by resolution of the Congress of Vienna. In 1903, it officially changed its name to the Grand Duchy of Saxony (German: Großherzogtum Sachsen), but this name was rarely used. The grand duchy came to an end in the German Revolution of 1918–19 with the other monarchies of the German Empire. It was succeeded by the Free State of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, which was merged into the new Free State of Thuringia two years later.
The full grand ducal style was Grand Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, Landgrave in Thuringia, Margrave of Meissen, Princely Count of Henneberg, Lord of Blankenhayn, Neustadt and Tautenburg.
The Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach branch has been the most genealogically senior extant branch of the House of Wettin since 1672.
Previous Page Next Page
دوقية ساكسونيا فايمر أيزيناخ الكبرى Arabic Саксен-Веймар-Айзенах BE Саксония-Ваймар-Айзенах Bulgarian Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach BR Saxònia-Weimar-Eisenach Catalan Sasko-výmarsko-eisenašské vévodství Czech Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach Danish Sachsen-Weimar-Eisenach German Saksio-Vajmaro-Eisenach EO Ducado de Sajonia-Weimar-Eisenach Spanish





