Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Tannic acid
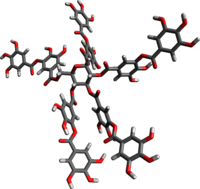
 Chemical structure of penta(digalloyl)glucose, a representative component of tannic acid
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-{3,4-dihydroxy-5-[(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy]benzoyl}-D-glucopyranose
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2,3-dihydroxy-5-({[(2R,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5,6-tetrakis({3,4-dihydroxy-5-[(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)carbonyloxy]phenyl}carbonyloxy)oxan-2-yl]methoxy}carbonyl)phenyl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 8186386 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.321 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C76H52O46 | |
| Molar mass | 1701.19 g/mol |
| Density | 2.12g/cm3 |
| Melting point | decomposes above 200 °C |
| 2850 g/L or 250 g/L[1][2] | |
| Solubility | 100 g/L in ethanol 1 g/L in glycerol and acetone insoluble in benzene, chloroform, diethyl ether, petroleum, carbon disulfide, carbon tetrachloride. |
| Acidity (pKa) | ca. 6 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Tannic acid is a specific form of tannin, a type of polyphenol. Its weak acidity (pKa around 6) is due to the numerous phenol groups in the structure. The chemical formula for commercial tannic acid is often given as C76H52O46, which corresponds with decagalloyl glucose, but in fact it is a mixture of polygalloyl glucoses or polygalloyl quinic acid esters with the number of galloyl moieties per molecule ranging from 2 up to 12 depending on the plant source used to extract the tannic acid. Commercial tannic acid is usually extracted from any of the following plant parts: Tara pods (Caesalpinia spinosa), gallnuts from Rhus semialata or Quercus infectoria or Sicilian sumac leaves (Rhus coriaria).
According to the definitions provided in external references such as international pharmacopoeia, Food Chemicals Codex and FAO-WHO tannic acid monograph only tannins obtained from the above-mentioned plants can be considered as tannic acid. Sometimes extracts from chestnut or oak wood are also described as tannic acid but this is an incorrect use of the term. It is a yellow to light brown amorphous powder.
While tannic acid is a specific type of tannin (plant polyphenol), the two terms are sometimes (incorrectly) used interchangeably. The long-standing misuse of the terms, and its inclusion in scholarly articles has compounded the confusion. This is particularly widespread in relation to green tea and black tea, both of which contain many different types of tannins not just exclusively tannic acid.[3]
Tannic acid is not an appropriate standard for any type of tannin analysis because of its poorly defined composition.
- ^ "Tannic acid". American Chemical Society. 15 January 2018.
- ^ "Tannic acid". Chemical Book.
- ^ Pettinga, C. (1979). "Darvon safety". Science. 204 (4388): 6. Bibcode:1979Sci...204....6P. doi:10.1126/science.432625. PMID 432625.
Previous Page Next Page


