Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Asparagine
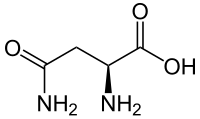 Skeletal formula of L-asparagine
| |||
 Skeletal formula of L-asparagine under physiological conditions
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Asparagine
| |||
| Other names
2-Amino-3-carbamoylpropanoic acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.019.565 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H8N2O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 132.119 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | white crystals | ||
| Density | 1.543 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 234 °C (453 °F; 507 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 438 °C (820 °F; 711 K) | ||
| 2.94 g/100 mL | |||
| Solubility | soluble in acids, bases, negligible in methanol, ethanol, ether, benzene | ||
| log P | −3.82 | ||
| Acidity (pKa) |
| ||
| -69.5·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Structure | |||
| orthorhombic | |||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−789.4 kJ/mol | ||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 219 °C (426 °F; 492 K) | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | Sigma-Alrich | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Asparagine (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N[2]) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+
3 form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain carboxamide, classifying it as a polar (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it. It is encoded by the codons AAU and AAC.
The one-letter symbol N for asparagine was assigned arbitrarily,[3] with the proposed mnemonic asparagiNe;[4]
- ^ Haynes WM, ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–89. ISBN 978-1498754286.
- ^ "Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides". IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. 1983. Archived from the original on 9 October 2008. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ "IUPAC-IUB Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature A One-Letter Notation for Amino Acid Sequences". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 243 (13): 3557–3559. 10 July 1968. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)34176-6. Archived from the original on 20 February 2024. Retrieved 21 February 2024.
- ^ Adoga, Godwin I; Nicholson, Bh (January 1988). "Letters to the editor". Biochemical Education. 16 (1): 49. doi:10.1016/0307-4412(88)90026-X. Archived from the original on 2024-02-20. Retrieved 2024-02-21.
Previous Page Next Page





