Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
Chronaxie
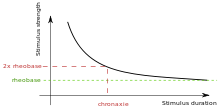
Chronaxie is the minimum time required for an electric current double the strength of the rheobase to stimulate a muscle or a neuron. Rheobase is the lowest intensity with indefinite pulse duration which just stimulated muscles or nerves.[1] Chronaxie is dependent on the density of voltage-gated sodium channels in the cell, which affect that cell's excitability. Chronaxie varies across different types of tissue: fast-twitch muscles have a lower chronaxie, slow-twitch muscles have a higher one. Chronaxie is the tissue-excitability parameter that permits choice of the optimum stimulus pulse duration for stimulation of any excitable tissue. Chronaxie (c) is the Lapicque descriptor of the stimulus pulse duration for a current of twice rheobasic (b) strength, which is the threshold current for an infinitely long-duration stimulus pulse. Lapicque showed that these two quantities (c,b) define the strength-duration curve for current: I = b(1+c/d), where d is the pulse duration. However, there are two other electrical parameters used to describe a stimulus: energy and charge. The minimum energy occurs with a pulse duration equal to chronaxie. Minimum charge (bc) occurs with an infinitely short-duration pulse. Choice of a pulse duration equal to 10c requires a current of only 10% above rheobase (b). Choice of a pulse duration of 0.1c requires a charge of 10% above the minimum charge (bc).
Previous Page Next Page


