Our website is made possible by displaying online advertisements to our visitors.
Please consider supporting us by disabling your ad blocker.
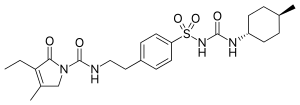
Glimepiride
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Amaryl, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a696016 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 100% |
| Protein binding | >99.5% |
| Metabolism | Complete Liver (1st stage through CYP2C9) |
| Onset of action | 2–3 hours |
| Elimination half-life | 5–8 hours |
| Duration of action | 24 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (~60%), feces (~40%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.170.771 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H34N4O5S |
| Molar mass | 490.62 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 207 °C (405 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Glimepiride is an antidiabetic medication within the sulfonylurea class, primarily prescribed for the management of type 2 diabetes.[1][2] It is regarded as a second-line option compared to metformin, due to metformin's well-established safety and efficacy.[1] Use of glimepiride is recommended in conjunction with lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise.[1] It is taken by mouth,[1] reaching a peak effect within three hours and lasting for about a day.[1]
Common side effects include headache, nausea, and dizziness.[1] Serious side effects may include low blood sugar.[1] Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended.[3] It works predominantly by increasing the amount of insulin released from the pancreas.[1] It is classified as a second-generation sulfonylurea.[4]
Glimepiride was patented in 1979 and approved for medical use in 1995.[5] It is available as a generic medication.[2] In 2022, it was the 64th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 10 million prescriptions.[6][7]
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Glimepiride Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ a b British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 693. ISBN 9780857113382.
- ^ "Glimepiride Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ Davis SN (2004). "The role of glimepiride in the effective management of Type 2 diabetes". J. Diabetes Complicat. 18 (6): 367–76. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2004.07.001. PMID 15531188.
- ^ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 449. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 10 January 2023. Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- ^ "The Top 300 of 2022". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 30 August 2024. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
- ^ "Glimepiride Drug Usage Statistics, United States, 2013 - 2022". ClinCalc. Retrieved 30 August 2024.
Previous Page Next Page


